Solutions to Strengthen Your IT Business Continuity Plan


The workflow of IT teams is ever-changing. Businesses must adapt quickly and use safeguards to prevent operation interruptions.
An IT business continuity program ensures normal business functions after a disaster or other disruptive event. Given society’s dependence on IT for daily needs, making sure that your IT infrastructure and systems operate without disruption is crucial in the face of disaster. Without a plan in place, companies risk financial losses, reputational damage, and long recovery times.
How confident are you that your IT department can maintain continuous uptime and availability during a crisis with minimal disruptions? This guide will help IT operatives identify those solutions as they begin developing or strengthening their IT business continuity plans.
An IT business continuity plan (IT BCP) is a specialized strategy that makes sure IT systems, infrastructure, and data remain resilient during and after major disruptions like natural disasters or cyberattacks. Unlike general business continuity plans that address broader areas like supply chain management, an IT BCP focuses on keeping an organization’s technical systems safe, including networks, servers, cloud services, and applications.
A strong IT BCP is able to:
IT BCPs protect organizations from risks such as:
An IT BCP also ensures regulatory compliance, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX, which have strict continuity measures. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and legal challenges.
For example, the 2024 CrowdStrike outage disrupted 8.5 million Windows devices, causing Fortune 500 companies to collectively incur an estimated $5.4 billion in uninsured damages. This highlights the need for a strong IT BCP to protect systems, maintain compliance, and prevent costly incidents.
Without a robust IT business continuity plan, companies risk financial losses, stress, and lasting reputational damage.
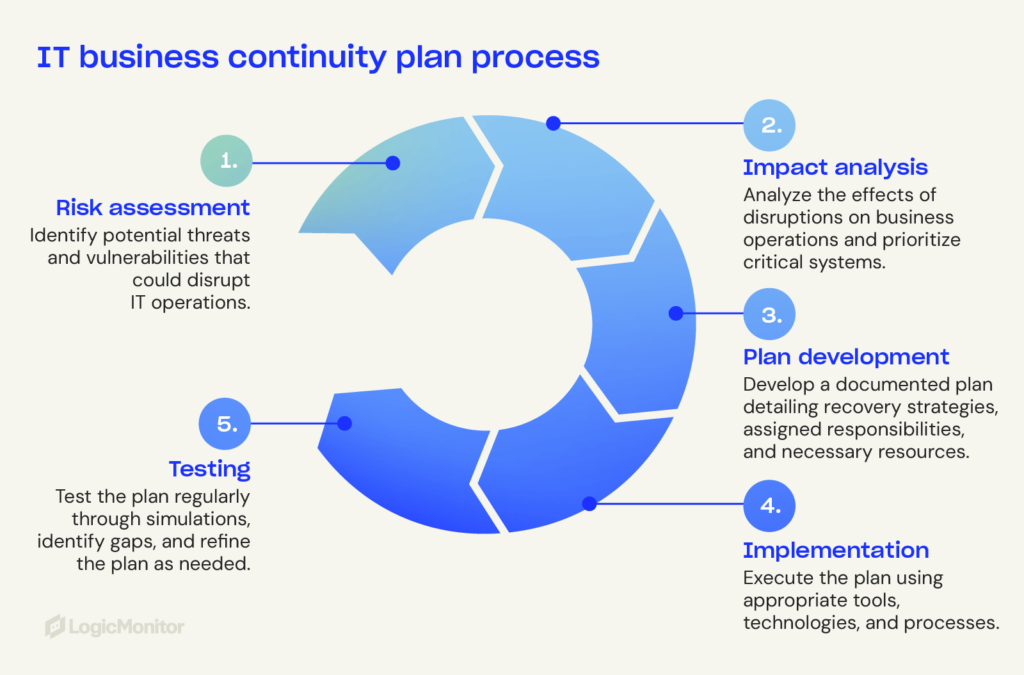
An effective IT BCP focuses on key components that strengthen systems and continue operations during disruptions.
Audits and risk protocols help organizations anticipate disruptions and allocate resources. Risk assessment identifies vulnerabilities like outdated hardware, weak security, and single points of failure.
Dependency mapping identifies relationships between IT systems, applications, and processes. For example, replicating databases is critical if failure disrupts multiple services. Understanding IT interconnections helps organizations identify critical dependencies and blind spots so they can plan recovery procedures.
Data backup and recovery are crucial for keeping information safe and quickly resuming operations after a significant disruption. Data recovery best practices include:
Failover systems maintain operations by automatically switching to backups during hardware or software failures. Examples of failover systems include:
Effective communication allows organizations to respond to an IT crisis. Strong IT BCPs include:
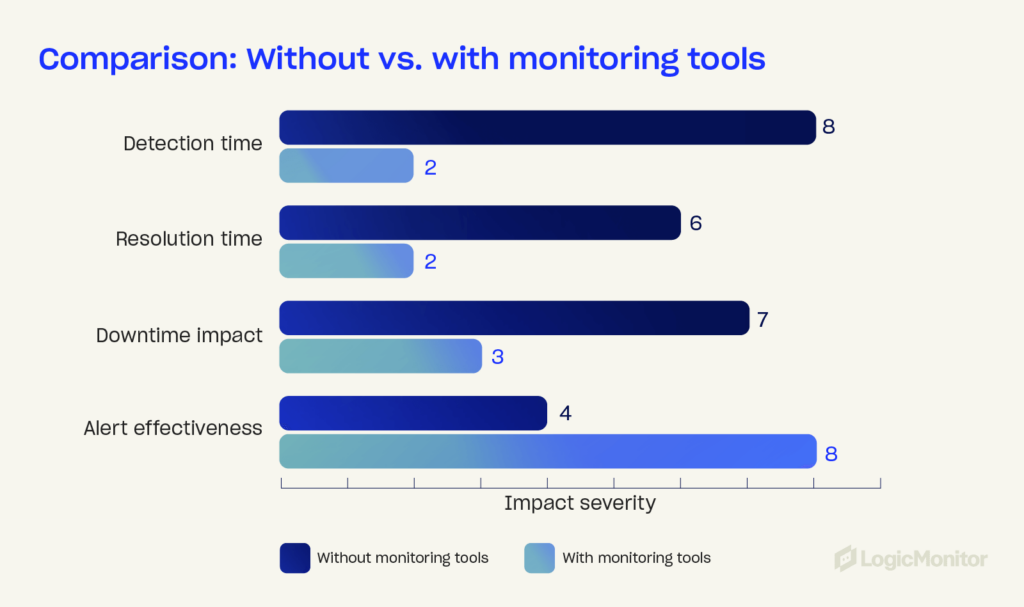
Tools that provide real-time insights and proactive alerts on system performance will find potential disruptions before they escalate. Routine simulation drills prepare employees for worst-case scenarios.
The rise in cyberattacks makes strong cybersecurity key to an IT BCP. Multi-factor authentication, firewalls, and endpoint protections guard systems against breaches, while incident response plans minimize attack damage.
Protect critical systems and ensure fast disruption recovery with these steps.
Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA) to evaluate how potential IT risks can affect your operations, finances, and reputation. Key BIA activities include:
Example: A financial services firm simulates a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack on its customer portal and identifies that its firewall rules need adjustment to prevent prolonged outages.
Not all IT systems and assets are equally important. Identify and prioritize systems that are vital in maintaining key business operations, including:
Example: A retail company classifies its payment processing systems as a Tier 1 priority, ensuring that redundant servers and cloud-based failovers are always operational.
Establish clear recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) to guide your strategy:
Example: A healthcare provider sets an RTO of 15 minutes for its electronic medical records system and configures AWS cross-region replication for failover.
Equip your organization with tools that support continuity and recovery efforts, including:
Example: A logistics company integrates Prometheus monitoring with an auto-remediation tool that reboots faulty servers when CPU spikes exceed a threshold.
An e-commerce company faces a ransomware attack that encrypts critical customer data.
The company recovers operations within 30 minutes, preventing major revenue loss and reputational damage.
Building an effective IT BCP requires advanced tools and technologies that ensure stability.
Modern infrastructure monitoring platforms are vital for detecting and eliminating disruptions. Tools such as AIOps-powered solutions offer:
Cloud solutions offer flexibility and scalability for IT continuity planning. Key benefits include:
Automation streamlines recovery processes and ensures IT infrastructure stays agile during crises. Examples include:
Robust cybersecurity is essential to IT continuity. Protect your systems with:
Even well-designed IT BCPs face obstacles. Understanding these common pitfalls will help you proactively address vulnerabilities and maintain operational strength.
Outdated or untested IT BCPs risk gaps or ineffective processes during a crisis. Regular updates will help you adapt to threats.
Modern IT systems rely heavily on external services like cloud providers, data centers, and software vendors. Failing to account for these dependencies can lead to significant disruptions during third-party outages or delays.
Even the most advanced IT systems require human intervention during a crisis. Human factors, such as unclear communication protocols and insufficient training, can compromise the execution of an IT BCP. Strategies for reducing human error include:
Financial limitations can keep organizations from creating effective continuity measures, like failover systems, backup solutions, or regular testing protocols. To address budget constraints:
As organizations adopt hybrid and multi-cloud systems, uninterrupted operations become a challenge. Issues like inconsistent configurations and siloed data can prolong disruptions and slow recovery. Regular audits, dependency mapping, and unified monitoring tools simplify crisis management and strengthen continuity.
Without support from leadership, BCP efforts can lack funding, strategic alignment, or organizational priority. Secure executive support by:
A strong IT business continuity plan ensures your operations remain resilient, even in unexpected disasters.
A strong IT BCP requires ongoing effort to remain effective against evolving threats. These practices ensure your plan stays effective during any crisis.
Regular tests can identify weaknesses in your IT BCP. Continuously improve processes to align with your current infrastructure and objectives. Testing methods include:
Regular training with clear responsibilities ensures team members understand their duties and can act quickly during disruptions.
Set measurable goals to evaluate your strategy’s effectiveness. Track performance against these benchmarks to ensure your plan meets its objectives:
An effective IT BCP must align with organizational goals. By working with teams across departments, you can:
Automation enhances the speed and efficiency of IT continuity efforts. Tools like monitoring platforms, automated failover systems, and AI-driven analytics reduce manual workloads and allow proactive problem-solving.
The threat landscape is constantly evolving. Regular risk assessments and real-time monitoring help identify emerging weaknesses before they escalate into major problems.
Regularly testing and refining your continuity plan is the key to staying prepared for any crisis.
Key trends shaping IT BCP include:
Stricter standards like GDPR, CCPA, and supply chain mandates require robust continuity plans.
Emphasizes restricted access, continuous authentication, and network segmentation to combat cyber threats.
An effective IT BCP is a strategic investment in your organization’s future. Identifying weaknesses, prioritizing critical systems, and using proactive measures reduce risks and maintain operations during disruptions.
Continuity planning isn’t a one-time task, however. As challenges like cyberattacks, regulatory changes, and shifting business needs evolve, an effective plan must adapt. Regular updates, testing, and cross-functional collaboration ensure your plan grows with your organization.
Ultimately, an effective IT BCP supports business success by protecting revenue, maintaining customer trust, and enabling operational stability. Taking these steps will prepare your organization to navigate future challenges confidently.
© LogicMonitor 2026 | All rights reserved. | All trademarks, trade names, service marks, and logos referenced herein belong to their respective companies.
