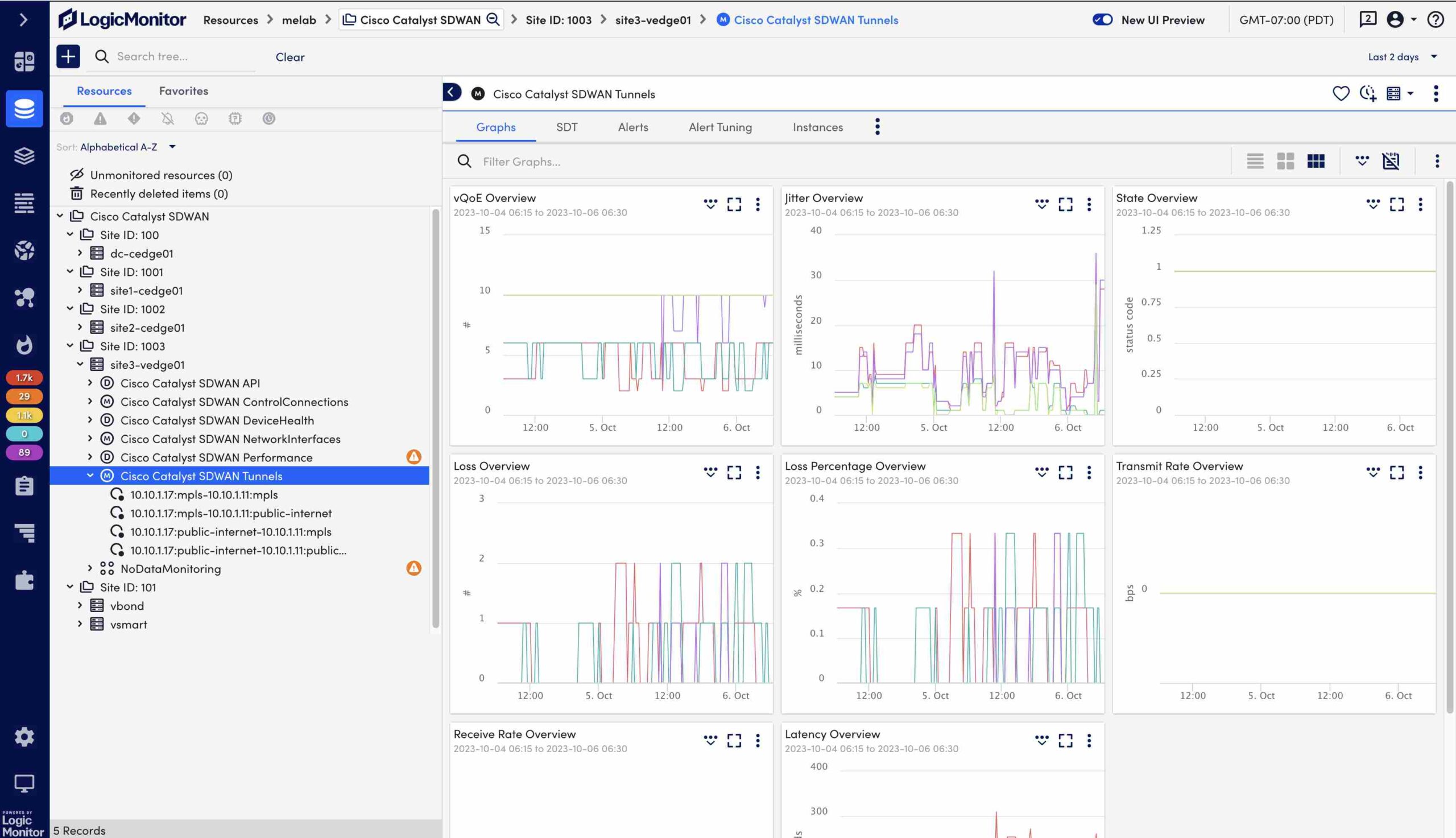
SD-WAN Monitoring Built for Hybrid Networks
Monitor SD-WAN performance across multi-vendor environments, detect anomalies in real time, and scale your network with confidence, no matter where your infrastructure lives.
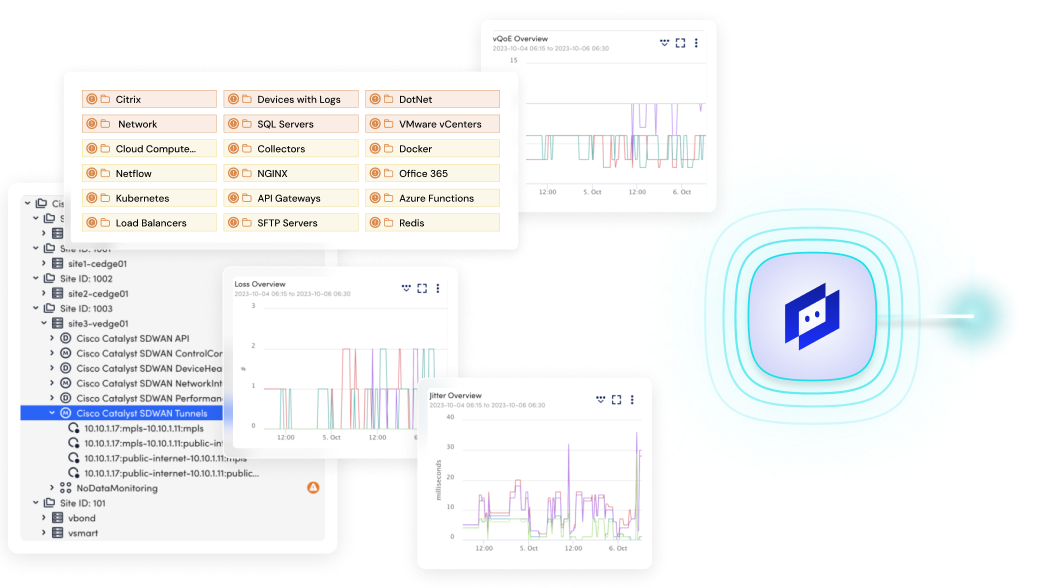

Monitor SD-WAN performance across multi-vendor environments, detect anomalies in real time, and scale your network with confidence, no matter where your infrastructure lives.

Get ahead of service-impacting issues with earlier warnings and faster incident response, so users stay connected and productivity stays high.
Maintain consistent performance across sites, clouds, and SD-WAN vendors as your network grows without losing visibility or control.
Make smarter choices about capacity, architecture, and spend with access to unified metrics, logs, and trends across your SD-WAN.
Eliminate blind spots across multi-vendor environments so your team can detect root causes faster and act with clarity and speed.
Automate alerting, eliminate noisy data, and streamline monitoring workflows, freeing your team to focus on optimization, not firefighting.
Maintain full visibility and performance awareness across on-prem, cloud, and edge environments even as your network evolves.
Observability powered by LogicMonitor Envision and Edwin AI
From dynamic path tracking and edge device visibility to unified alerts and multi-vendor support, LM Envision gives you full control over your SD-WAN environments.
Unify monitoring across Cisco, Meraki, Palo Alto Prisma, Fortinet, and more without separate tools or manual integration.
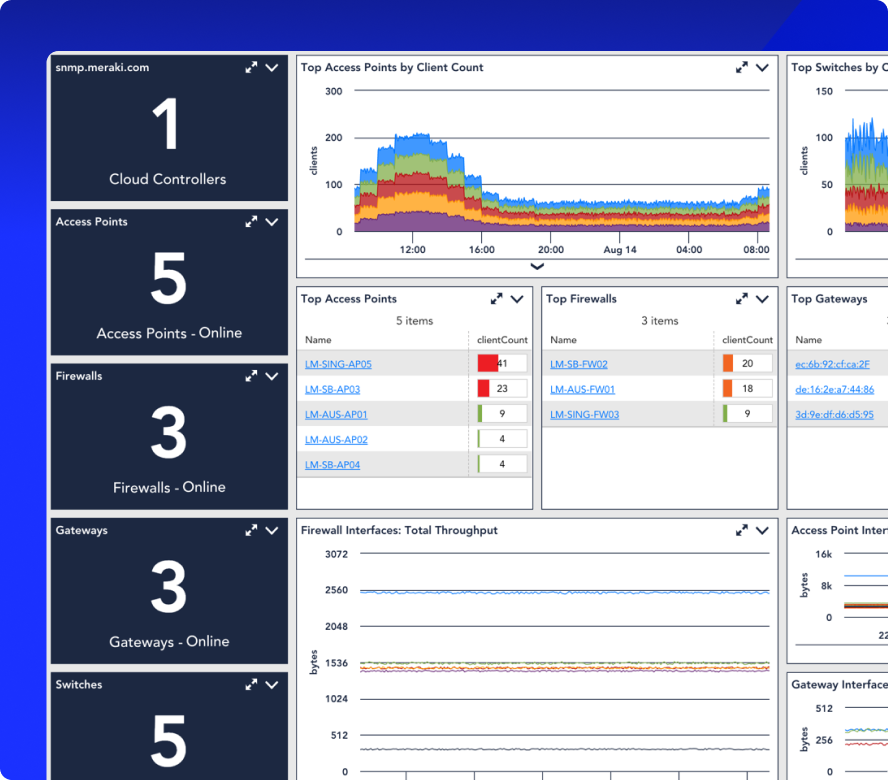
Detect tunnel degradation, jitter, latency, and packet loss before they disrupt connectivity or application performance.
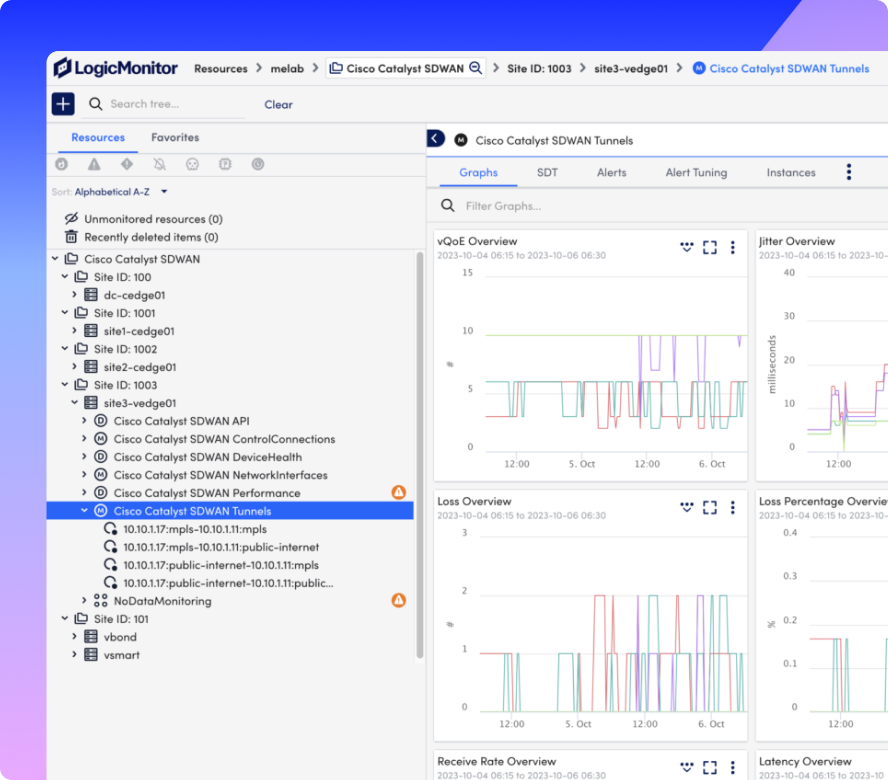
Combine structured logs and performance data to accelerate root cause analysis and reduce MTTR.
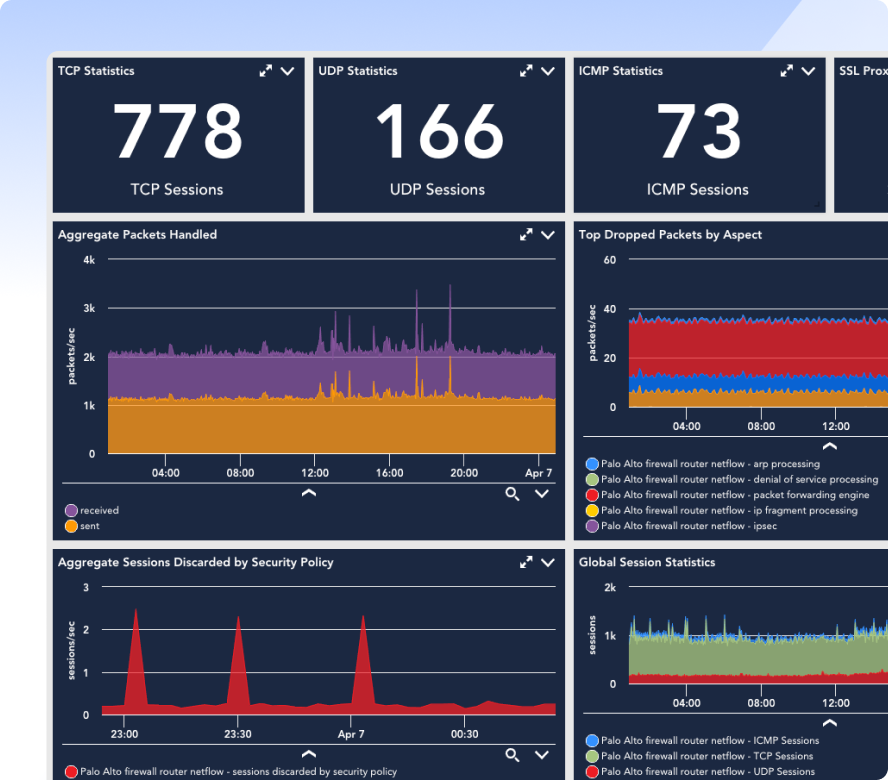
Route the right alerts to the right teams at the right time with integrations for ITSM, chat, and automation platforms.
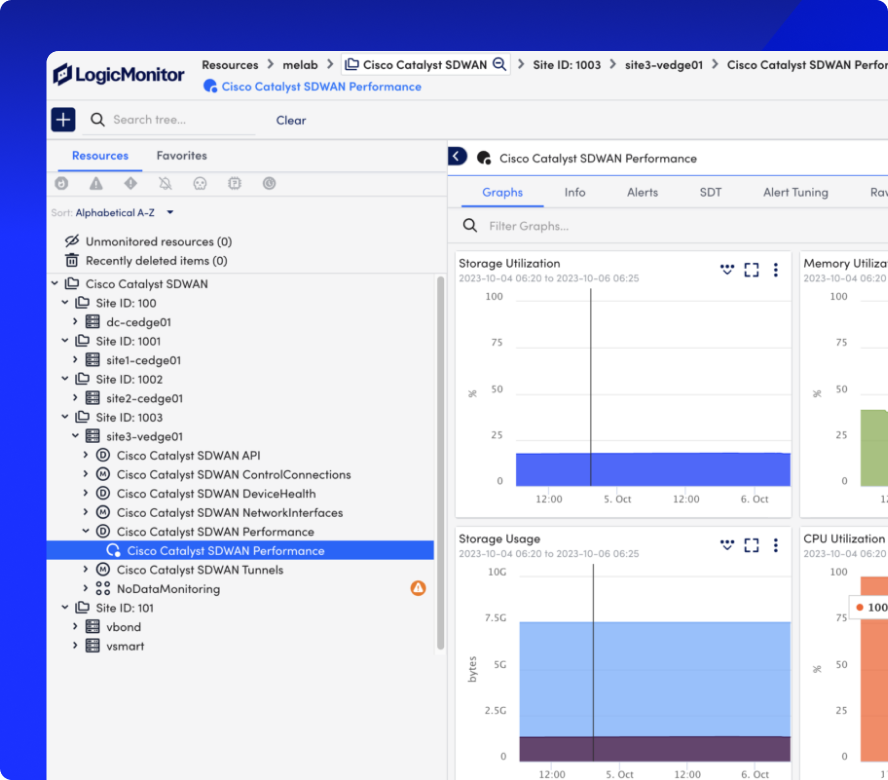
Leverage predictive analytics to anticipate bandwidth constraints and guide infrastructure investments.
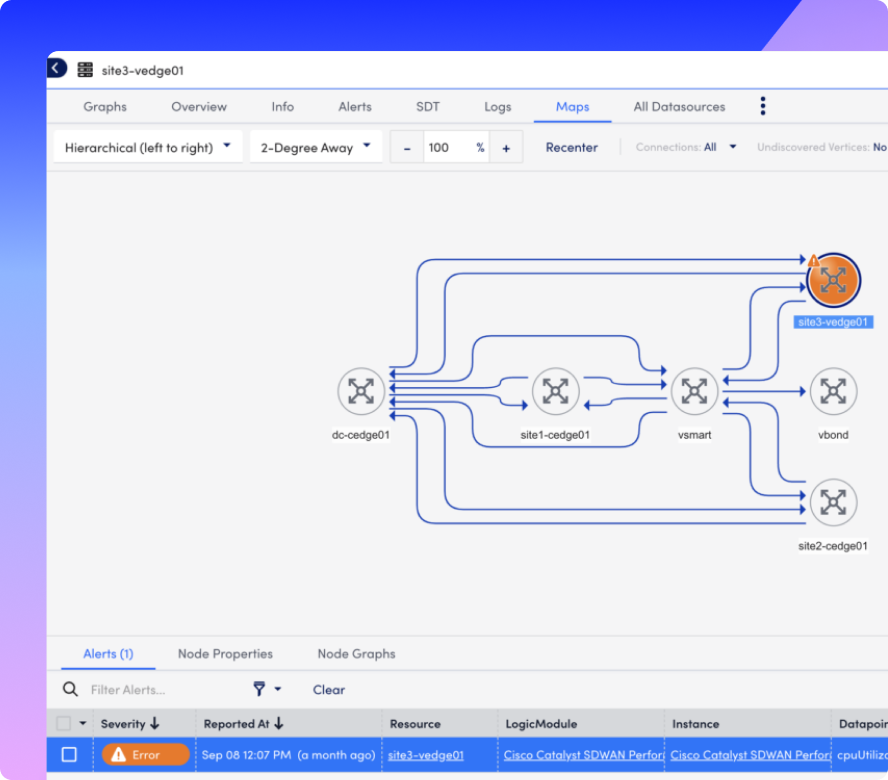
Integrations
LM Envision integrates with your entire SD-WAN stack, including Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela), Meraki, Palo Alto Prisma, Fortinet, Juniper, VMware, and more. Whether you’re standardizing or managing multi-vendor networks, LogicMonitor keeps every connection observable, every device in view, and every alert in context.
100%
collector-based and API-friendly
3,000+
integrations and counting

AI AGENT FOR ITOPS
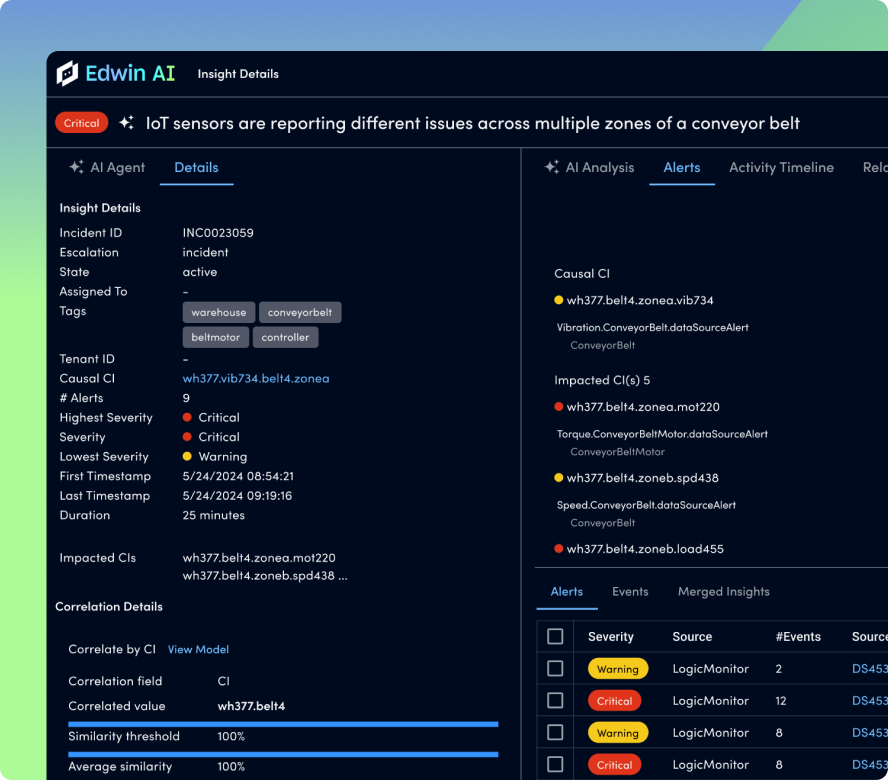
Edwin AI automatically detects tunnel degradation, correlates anomalies across branches and vendors, and summarizes incidents in plain language, so your teams don’t waste time chasing alerts. From predicting bandwidth constraints to pinpointing root cause, Edwin brings clarity and speed to every decision.
67%
ITSM incident reduction
88%
noise reduction
BY THE NUMBERS
GET ANSWERS
Get the answers to the top SD-WAN monitoring questions.
Yes. LM Envision provides out-of-the-box support for Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela), Meraki, Palo Alto Prisma SD-WAN, Fortinet, VMware, and more. You can monitor performance, tunnel health, and edge devices across vendors—all from a single platform.
Absolutely. LM Envision monitors SD-WAN tunnel quality metrics in real time, including jitter, latency, packet loss, and throughput, so you can detect degradation before it impacts user experience.
Yes. LM Envision integrates with tools like ServiceNow, PagerDuty, Slack, Microsoft Teams, and more. You can automate alert routing, streamline escalation workflows, and reduce response times.
Most teams begin monitoring in under five minutes using LogicMonitor’s agentless onboarding. Built-in integrations and auto-discovery make it easy to get up and running fast—no heavy setup required.
With Edwin AI, LM Envision automatically correlates alerts across tunnels, locations, and devices, reducing noise and highlighting root cause. You’ll only see what matters when it matters.
Yes. LM Envision provides predictive insights based on historical usage trends, so you can plan bandwidth expansion, anticipate tunnel capacity limits, and guide strategic infrastructure decisions.