SNMP Traps LogSource Configuration
Last updated - 12 February, 2026
SNMP Traps type LogSource enables the LogicMonitor Collector to ingest SNMP traps into LogicMonitor logs without configuring alerts.
Requirements for Configuring SNMP Traps LogSource
- EA Collector 34.500 or later version installed on your machine. For more information, see Managing Collectors.
Configuration Options
The configuration option includes configuration details specific to the SNMP Traps LogSource. For more information, see Configuring a LogSource.
Note: LogicMonitor has removed the Enterprise OIDs field. Starting with EA Collector 35.300, Enterprise OIDs are not required to translate SNMP traps. However, SNMP Traps translation will still work for all the out-of-the-box enterprises/MIBs supported by LogicMonitor.
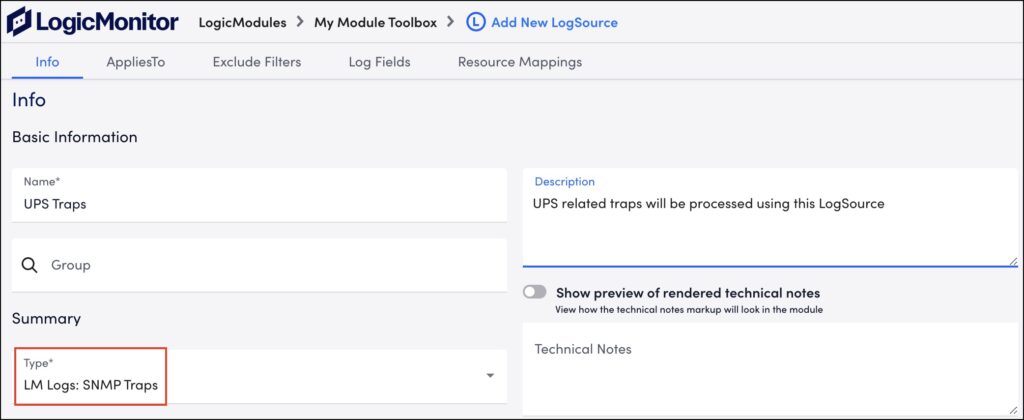
Info
Select “LM Logs: SNMP Traps” from the Type dropdown menu and provide basic information such as name, group name, description, and technical notes.
AppliesTo
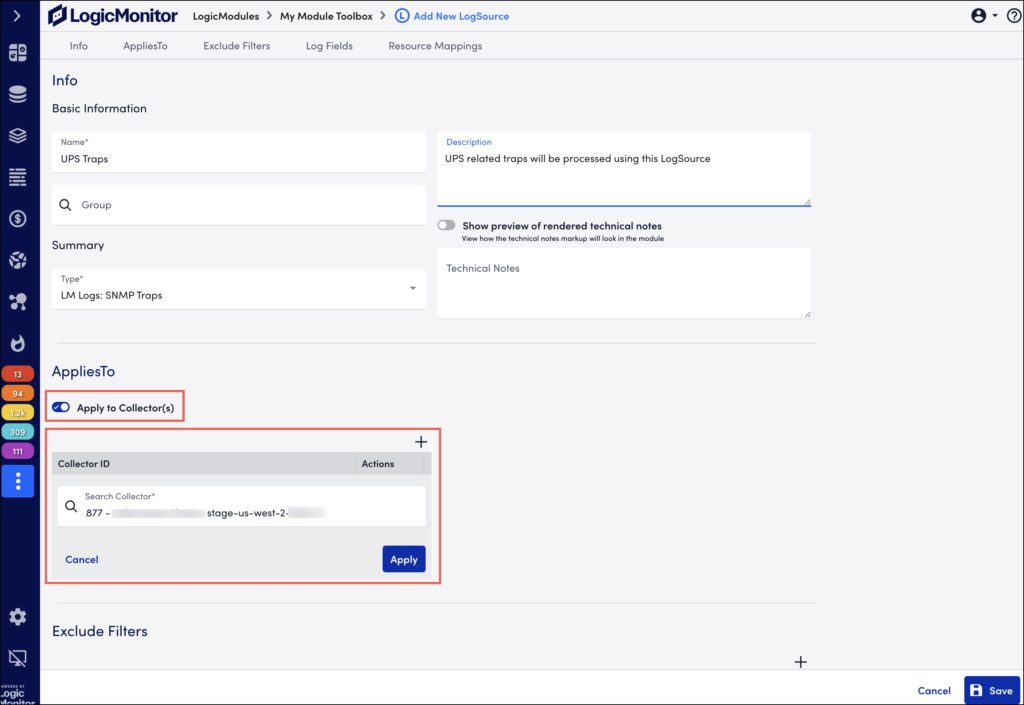
Applying LogSource on a Collector
With EA Collector 35.200 or later, you can apply LogSource to a Collector directly using the Apply to Collector(s) option. By default, the Apply to Collector(s) option is disabled.
Applying LogSource on the Collector is useful in the following scenarios:
- The Collector does not monitor the device which is forwarding the SNMP traps to the Collector.
- LogicMonitor does not monitor the device which is forwarding the SNMP traps to the Collector.
For a device that forwards the SNMP traps to a Collector, perform the following steps to apply a LogSource to a Collector.
- Add the SNMP community (for the SNMP v1/v2 traps) or the SNMP credentials (for the SNMP v3 traps) as Collector (self-monitoring device) properties to enable the Collector to authenticate the traps forwarded to it. For more information, see Defining community strings and SNMP credentials for Ingestion of SNMP traps as LM Logs.
- Create a LogSource and enable the Apply to Collector(s) option to apply the LogSource on the Collector.
Note:
- The AppliesTo section lists only the self-monitoring Collectors that have EA Collector 35.200 or later installed.
- Only one LogSource of SNMP Traps type can be applied to a self-monitoring Collector.
- If a device is monitored by the Collector that receives traps, then the LogSource that is applied on the device is preferred over the LogSource applied on the Collector. For more information, see the SNMP Traps Processing Preference section.
Exclude Filters
For Collector versions released prior to EA Collector 36.400, traps that match with the exclude filters criteria are not ingested.
With EA Collector 36.400 and later, traps that match with any of the exclude filters criteria are not ingested. You can use the following filters to exclude SNMP traps.
Available Parameters
| Attributes | Comparison Operator | Value Example | TrapOID Example | Varbind Key Example | Varbind Value Example | Description |
| TrapOID | Equal, NotEqual, StartsWith | 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.61.2.0.1 | – | – | – | Trap OID of the trap |
| Varbind | RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch | 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.13.1.3.1.2 | 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.61.2.0.1 | 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.13.1.3.1.2 | [a-z]+ | TrapOID with Varbind key and value of the trap |
Log Fields
You can configure Log Fields (tags) to add metadata to the log entry.
Available Parameters
| Method | Key Example | Value Example | Description |
| Static | Customer | Customer_XYZ | Key and value is added as is to the log entry metadata |
| LM Property(Token) | Device | ##system.deviceId## | The device ID value extracted from the device property in LogicMonitor |
Resource Mappings
For resource mapping you can configure LM log key to match a monitored resource’s LM property.
Available Parameters
| Method | Key Example | Value Example | Description |
| Static | Customer_Id | 1219 | Key and value is used as is for resource mapping. |
| IP | system.ips | 10.20.30.40 | Use the SNMP trap host field information and resolve it to IP. The Value field is disabled if you select this method. You can only enter a key. |
| FQDN | system.hostname | application.service.example.com | Fully Qualified Domain Name, from DNS resolution of hostname received from the host address of the trap. The Value field is disabled if you select this method. You can only enter a key. |
| HOSTNAME | system.hostname | host1.example.com | The Value field is disabled if you select this method. You can only enter a key. |
| HOST WITHOUT DNS | system.hostname | host1 | The Value field is disabled if you select this method. You can only enter a key. |
For correct resource mapping, it is essential to know how the source (host) address is extracted from the trap based on the SNMP trap version and how it is forwarded to the Collector device.
Starting with EA Collector 36.100, based on the SNMP trap version, the Collector uses the host address from the following elements of the trap PDU.
| SNMP Trap Version | PDU Element |
|---|---|
| v1 | agent-addr |
| v2c and v3 | Value of variable binding OID ‘1.3.6.1.6.3.18.1.3’ (SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB.snmpTrapAddress) |
Note: If the PDU elements (given in the table above) from the respective SNMP trap versions are not present in the trap, then the peer address (socket address) of the trap is used for resource mapping. The socket address contains the address of the device which forwards the trap to the Collector device. When the trap generating device forwards the trap through intermediate devices, the socket address contains the address of the last device which forwarded the trap to the Collector. This is explained in the following example.
Example
Scenario—Traps are forwarded from one device to another before reaching the Collector device.
- Device A (Trap generating device)—The device that generates the SNMP trap. The IP address of this device is 192.168.1.10.
- Device B (Trap forwarding device)—The device that receives the trap from Device A and forwards it to the trap Collector device. The IP address of this device is 192.168.1.20.
- Device C (Trap Collector device)—The Collector device where traps are collected and monitored.
SNMP v1 Trap
- Agent Address—The IP address of the device that generates the SNMP trap (that is, Device A) is included in the agent-addr field of the trap message.
- Trap Forwarding—When the Device B forwards the trap to Device C, typically, the Device B uses the Device C’s address as the destination address for the trap, but the agent-addr field still contains the Device A’s IP address.
SNMPv1 Trap Packet Example
PDU Type: Trap
Agent Address (agent-addr): 192.168.1.10 (Device A’s IP)
Variable Bindings: ... SNMP v2c and v3 Trap
- Variable Bindings—The agent-addr is part of the trap’s variable bindings. The agent-addr variable is explicitly included as one of the OID-value pairs in the trap message.
- Trap Forwarding—When the Device B forwards the trap, it includes Device A’s IP address in the variable bindings. As a result, the Device C can view the IP address in the trap message.
SNMP v2c and v3 Trap Packet Example
PDU Type: Trap
Variable Bindings:
1.3.6.1.6.3.18.1.3.0 (agent-addr): 192.168.1.10 (Device A’s IP)
...You can observe that for all the supported SNMP versions, when the Device B forwards the traps to Device C, it retains the Device A’s IP address in the relevant field (agent-addr for SNMP v1 and a variable binding for SNMP v2c and v3), ensuring that the Device C knows the original source of the trap.
If the agent-addr is missing or empty for v1 traps, or if the specified variable binding is missing for SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 traps, the Collector device uses the socket address which is Device B’s address (192.168.1.20) for resource mapping.
SNMP Traps LogSource Configuration Example
The following is an example of SNMP Traps LogSource configuration.
Basic Information
| Field Name | Value Example |
| Name | SNMP Traps LogSource |
| Group | SNMP Trap LogSources |
| Type | LM Logs: SNMP Traps |
| Description | UPS related traps will be processed using this LogSource |
| AppliesTo | (custom query) isLinux() || isNetwork() |
Exclude Filters
| Attribute | Comparison Operator | Value |
| TrapOID | Equal | 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.61.2.0.1 |
Log Fields
| Method | Key | Value |
| Static | Customer | Customer_xyz |
Resource Mappings
| Method | Key | Value |
| LM Property(Token) | system.deviceId | ##system.deviceId## |
Processing SNMP Traps using LogSource and EventSource
Collector processes SNMP traps using LogSource or EventSource. At a time, either LogSource or EventSource is used and under any scenario, both cannot be used simultaneously.
- Processing SNMP traps using LogSource—If a Collector monitors a device with LogSource applied on it, the Collector processes the SNMP traps only from devices on which LogSource is applied. Collector ignores (that is, does not process) traps from devices that do not have LogSource applied on them.
- Processing SNMP traps using EventSource—If LogSource is not applied on all the devices monitored by a Collector, but EventSource is applied on them, the Collector processes the SNMP traps from devices on which EventSource is applied.
Review the following scenarios to understand how Collector processes SNMP traps. In these scenarios, LogicMonitor has considered 3 devices monitored by the same Collector.
Scenario 1
The Collector processes SNMP traps from both Device 1 and Device 3 only using LogSource as there is at least one device with LogSource applied on them.
The SNMP traps from Device 2 are ignored (that is, not processed) as LogSource is not applied on Device 2.
| Device | Is LogSource Applied | Is EventSource Applied |
| Device 1 | Yes | Yes |
| Device 2 | No | Yes |
| Device 3 | Yes | No |
Scenario 2
The Collector processes SNMP traps from both Device 1 and Device 2 only using EventSource as none of the devices have LogSource applied on them. The SNMP traps from Device 3 are ignored (that is, not processed) as Device 3 does not have EventSource applied on it.
| Device | Is LogSource Applied | Is EventSource Applied |
| Device 1 | No | Yes |
| Device 2 | No | Yes |
| Device 3 | No | No |
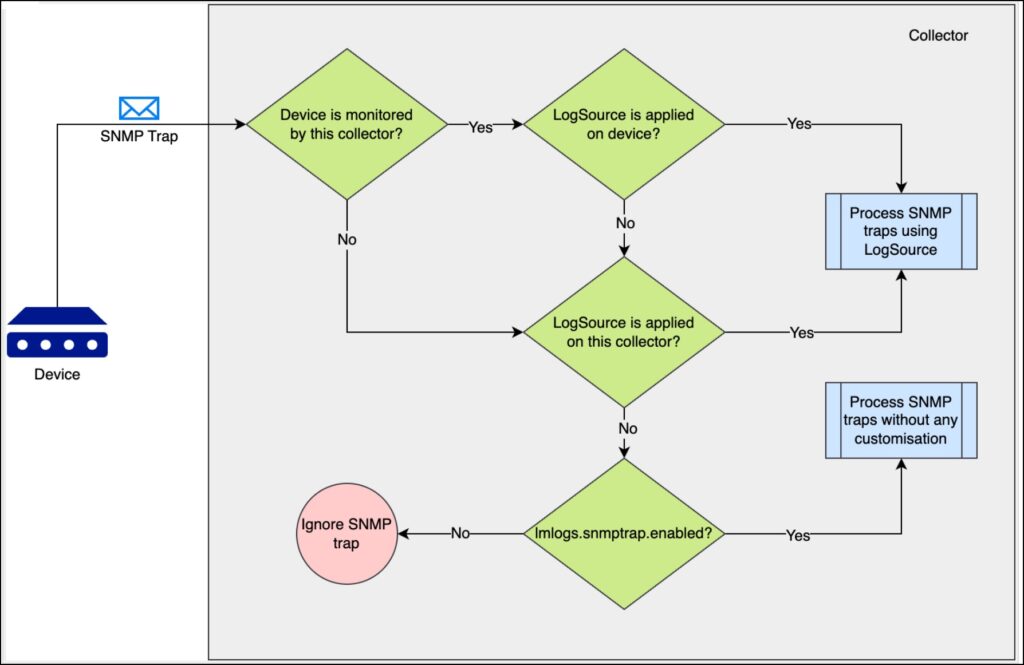
SNMP Traps Processing Preference
With the capability to apply LogSource on a Collector, depending on the customer requirement, there are three ways in which the Collector can process the SNMP traps.
- To ingest the SNMP traps received by the collector—Enable the
lmlogs.snmptrap.enabledproperty in the agent.conf settings. Alternatively, you can select the Enable log collection for Syslog and SNMP trap option on the Add Collector page to enable this property. Once enabled, the Collector ingests all the SNMP traps without any customisation such as filters, resource mapping, and so on. - To add customisations—For customisations such as filtering traps or adding a different method for resource mapping, a LogSource should be created and applied on the Collector that receives the SNMP trap by enabling the Apply to Collector(s) option on the LogSource.
- To handle the SNMP traps from a device using a specific LogSource definition—A usual LogSource must be applied on the device which is forwarding the SNMP traps to the Collector.
A usual LogSource that is applied on a device is preferred over the LogSource applied on a Collector for processing the SNMP traps.
A LogSource that is applied on a Collector is preferred over Collector’s agent.conf property lmlogs.snmptrap.enabled for processing the SNMP traps.
Note: In a LogSource, where the ApplyTo Collector(s) switch is enabled, to ensure smooth functioning, you must select Collectors that are not part of an Auto-Balanced Collector Group (ABCG).
You can review the following scenarios to understand the preference in which the Collector (that receives the SNMP traps) processes the SNMP traps.
| Scenario # | Is the device monitored by the collector* | Is a usual LogSource applied on the device | Is a LogSource applied on the collector using the Apply to Collector(s) switch | Is lmlogs.snmptrap.enabled set to true | Result |
| 1 | Yes | Yes | Any(Yes/No) | Any(Yes/No) | SNMP traps are processed using the usual LogSource applied on the device which is forwarding the SNMP traps. |
| 2 | Yes | No | Yes | Any(Yes/No) | SNMP traps are processed using the LogSource applied on the Collector which is receiving the SNMP traps. |
| 3 | No | Any(Yes/No) | Yes | Any(Yes/No) | SNMP traps are processed using the LogSource applied on the Collector which is receiving the SNMP trap |
| 4 | No | Any(Yes/No) | No | Yes | SNMP traps are processed using the lmlogs.snmptrap.enabled property in the agent.conf settings of the Collector which is receiving the SNMP traps. |
* A Collector monitors a device in the following 2 scenarios:
- On the Manage Resource page, the Collector is assigned as a Preferred Collector to the device.
- On the Manage Resource page, the Collector is assigned as a Log Collector using the Set LM Logs Collector option.
Translating SNMP Traps using Custom MIBs
Starting with EA Collector 35.400 release, you can use the MIBs to JSON Converter Utility to convert the MIB files to JSON files. In a Collector, the utility is located at [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/bin/snmpMibsToJsonConversionUtil.
This Python-based utility is designed to convert the custom MIBs (which LogicMonitor does not support out-of-the-box) to enterprise JSON files, which the collector then uses to translate the SNMP traps. By default, the enterprise JSON files are placed in the [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/snmpdb/custom directory.
How SNMP Trap Translation Works
SNMP traps are received as a blob of data in the form of an SNMP Protocol Data Unit (PDU). The PDU contains multiple elements which are initially encoded. After decoding the SNMP trap PDU, LogicMonitor gets various elements of metadata associated with the SNMP trap, an Object Identifier (OID) representing the type of trap, and a series of variable bindings (varbinds) which are a list of pairs where each pair consists of an OID and its corresponding value.
The SNMP trap translation serves the following purpose:
- It provides human readable values enclosed in parentheses immediately adjacent to the OIDs contained in the SNMP trap captured by LM Logs.
- It maps the human readable values as fields associated with the SNMP trap along with their corresponding values. These fields can be used in filters and queries in the LM Logs platform, and in log pipelines and alert conditions.
Example
Elements of SNMP Trap PDU
Trap Oid => 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.276.0.1
Variable Binding 1 => 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1=5
Variable Binding 2 => 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2=GigabitEtherenet1/0/5
Variable Binding 3 => 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8=2
Variable Binding 4 => 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.7=3
Starting with EA Collector 36.200, to format the SNMP trap messages as JSON, you can set the lmlogs.snmptrap.formatMessageAsJson.enabled property to true in the agent.conf settings. By default, this property is set to false. Also, the translated variable binding keys of the SNMP trap are included in a single log field, instead of individual log fields for each translated variable binding key.
If the lmlogs.snmptrap.formatMessageAsJson.enabled property is set to false
SNMP trap ingested as LM Log after translationMessage => trapOid=1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.276.0.1(cieLinkDown) 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1(ifIndex)=5 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2(ifDescr)=GigabitEtherenet1/0/5 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8(ifOperStatus)=2(down) 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.7=3
Apart from the message field, the translated variable binding keys of the SNMP trap are included in individual log fields for each translated variable binding key along with the respective values. If the variable binding value is not translated, the field will include the raw variable binding value. In this example, the following fields are present in the log:
| Log Field | Value |
| ifIndex | 5 |
| ifDescr | GigabitEtherenet1/0/5 |
| ifOperStatus | down |
If the lmlogs.snmptrap.formatMessageAsJson.enabled property is set to true
The SNMP trap messages are formatted as JSON.
{
"trapOID": {
"value": "1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.276.0.1",
"name": "cieLinkDown"
},
"1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1": {
"name": "ifIndex",
"value_raw": "5"
},
"1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2": {
"name": "ifDescr",
"value_raw": "GigabitEtherenet1/0/5"
},
"1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8": {
"name": "ifOperStatus",
"value_raw": "2",
"value_desc": "down"
},
"1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.7": {
"value_raw": "3"
}
}The translated variable binding OIDs are included in a single log field varbinds instead of individual log fields.
| Log Field | Value |
varbinds | {"ifIndex":"5","ifDescr":"GigabitEtherenet1/0/5","ifOperStatus":"down"} |
Note:
- Irrespective of whether you set the value of the lmlogs.snmptrap.formatMessageAsJson.enabled property to true or false, the
Variable Binding 4 => 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.7=3is not included in the log fields, as the OID of this variable binding (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.7) is not translated. - SNMP traps are translated irrespective of the SNMP trap version.
Requirements for Using the Utility
- Custom MIB files along with all its dependencies or parent MIB files.
- You must have Python version between 3.8 to 3.12 installed on your machine.
- To translate traps from the converted JSON files generated by the utility, the Collector service user must have
readaccess to the JSON files. - To run the utility, you must have
readaccess to the source directory (the directory that contains MIBs) andwriteaccess to the destination directory (the directory that stores the JSON files). - Ensure that the definition of a MIB file is not part of multiple input MIB files. If it is, the utility will consider either of such files. For example, for the ABC MIB, there must not be multiple files with the below line
ABCDEFINITIONS ::= BEGIN - Install the dependencies of the utility. To do so, go to the utility directory [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/bin/snmpMibsToJsonConversionUtil/ and run the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtHow the Utility Generates the JSON Files
- Run the
snmpMibsToJsonConverter.pyfile provided in the utility directory. - Specify the directory path where the custom MIB files are placed.
- Specify the directory path to generate the converted JSON files. By default, the files are generated in the default directory [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/snmpdb/custom. However, you can specify a different directory.
- The utility converts the MIB files and generates the JSON files in the directory that you specified.
Note: Do not rename the JSON files.
- If the JSON files are generated in a different directory, copy the files to the default directory [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/snmpdb/custom.
- When the collector restarts, the collector uses the JSON files to translate the corresponding SNMP traps.
Note: For the common enterprise JSON files present in both the [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/snmpdb/core and the [LogicMonitor Collector Directory]/snmpdb/custom directories, if common traps or OIDs are present in these JSON files, the SNMP traps are translated using the JSON file present in the custom directory. For exclusive traps or OIDs, the SNMP trap translation works as per the corresponding JSON file.
To troubleshoot utility issues, see Troubleshooting MIBs to JSON Converter Utility Issues.
If you have questions or face any issues while using the utility, contact your LogicMonitor Customer Success Manager (CSM).


